ac Transducer Function
Select products that include an ac Transducer function.
Please refer ac Input Conditioning for articles ac measurement.
Find ac Transducer select ⇒ Input ⇒ Output
- ac A
- ac A, Select Output
- 4-20mA 2-Wire
- ac A 4-20mA 2-Wire, Select Product
- ACT241 ac Current Transducer

- 4-20mA 4-Wire
- ac A 4-20mA 4-Wire, Select Product
- SL345 AC and Bipolar Isolator
- DCT247 Dc Current Transducer
- ACT284 ac Transducer
- ACT141 ac Current Transducer

- dc mA/V 3-Wire
- ac A dc mA/V 3-Wire, Select Product
- ACT241 ac Current Transducer

- dc mA/V 4-Wire
- ac A dc mA/V 4-Wire, Select Product
- SL345 AC and Bipolar Isolator
- DCT247 Dc Current Transducer
- ACT284 ac Transducer
- ACT141 ac Current Transducer


- ac Power
- ac Power, Select Output
- 4-20mA 4-Wire
- ac Power 4-20mA 4-Wire, Select Product
- AWT190 Ac Active Power Transducer
- ART191 Ac Active VAR Transducer
- AVAT192 ac Active VA Transducer
- APT193 Ac Active Phase Angle Trans.

- dc mA/V 4-Wire
- ac Power dc mA/V 4-Wire, Select Product
- AWT190 Ac Active Power Transducer
- ART191 Ac Active VAR Transducer
- AVAT192 ac Active VA Transducer
- APT193 Ac Active Phase Angle Trans.

- Bipolar
- ac Power Bipolar, Select Product
- AWT190 Ac Active Power Transducer
- ART191 Ac Active VAR Transducer
- AVAT192 ac Active VA Transducer
- APT193 Ac Active Phase Angle Trans.


- ac V
- ac V, Select Output
- 4-20mA 2-Wire
- ac V 4-20mA 2-Wire, Select Product
- AVT245 ac Voltage Transducer

- 4-20mA 4-Wire
- ac V 4-20mA 4-Wire, Select Product
- SL345 AC and Bipolar Isolator
- SL350 Pulse Frequency Transmitter
- ACT284 ac Transducer
- AVT145 Ac Voltage Transmitter

- dc mA/V 3-Wire
- ac V dc mA/V 3-Wire, Select Product
- AVT245 ac Voltage Transducer

- dc mA/V 4-Wire
- ac V dc mA/V 4-Wire, Select Product
- SL345 AC and Bipolar Isolator
- SL350 Pulse Frequency Transmitter
- ACT284 ac Transducer
- AVT145 Ac Voltage Transmitter

- Relay
- ac V Relay, Select Product
- VPR271 Voltage Presence Relay


- dc A
- dc A, Select Output
- 4-20mA 4-Wire
- dc A 4-20mA 4-Wire, Select Product
- SL345 AC and Bipolar Isolator
- DCT247 Dc Current Transducer

- dc mA/V 4-Wire
- dc A dc mA/V 4-Wire, Select Product
- SL345 AC and Bipolar Isolator
- DCT247 Dc Current Transducer


- dc mA/V
- dc mA/V, Select Output
- 4-20mA 4-Wire
- dc mA/V 4-20mA 4-Wire, Select Product
- SL345 AC and Bipolar Isolator

- dc mA/V 4-Wire
- dc mA/V dc mA/V 4-Wire, Select Product
- SL345 AC and Bipolar Isolator


- Signal Powered
- Signal Powered, Select Output
- Relay
- Signal Powered Relay, Select Product
- VPR271 Voltage Presence Relay


- Speed/ Frequency/ Pulse
- Speed/ Frequency/ Pulse, Select Output
- 4-20mA 4-Wire
- Speed/ Frequency/ Pulse 4-20mA 4-Wire, Select Product
- SL350 Pulse Frequency Transmitter

- dc mA/V 4-Wire
- Speed/ Frequency/ Pulse dc mA/V 4-Wire, Select Product
- SL350 Pulse Frequency Transmitter


- Select an Input (above)

Select products that include an ac Transducer function.
Please refer ac Input Conditioning for articles ac measurement.

About ac Transducer
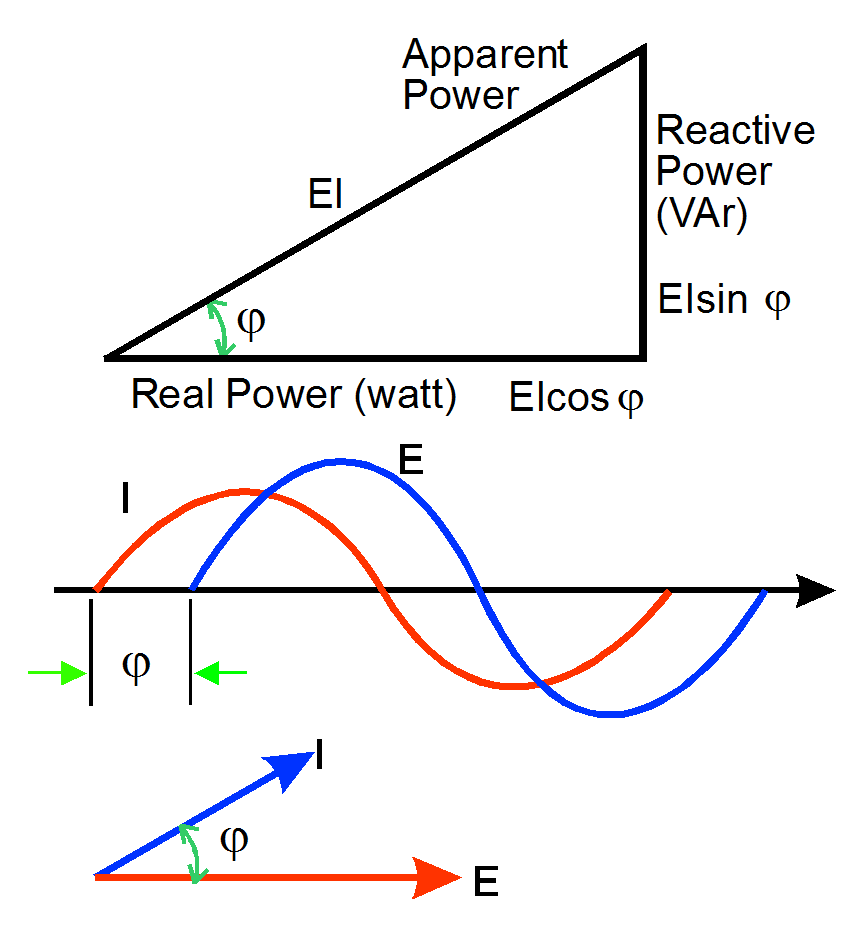
An ac transducer is used to change an electrical quantity such as voltage, current, power or frequency into a proportional dc output.
By means of a transducer, a complex electrical quantity, such as watts, can be measured at a convenient location and converted into a load independent dc current signal for transmission over two wires over any distance for display, recording or control.
For remote indication of watts or vars, a transducer can reduce the number of signal wires to be laid between source and indicator from as many as nine to two.
Transducer output wires need only be insulated for low voltage and have small cross-sectional area. Such lines are easily run and effect savings in terms of cable costs and space occupied on cable trays and the connecting and terminating elements required.
- Active Transducers
- Active Transducers need an auxiliary power supply.
- Passive Transducers
- Passive Transducers are signal powered no auxiliary supply is needed.
- Class 0.5 means
-
- inaccuracy of the transducer is less than 0.5% of the span.
- non-linearity is less than 0.5% of the span.
- ripple (peak-peak) is less than 0.5% of the span.
- response time is less than 500 msec.
Typical Features of APCS ac Transducers
- Australian designed and manufactured (for local support).
- Fully meets standards AS1384, BS6253, IEC688.
- Prompt delivery of standard items or specials which can be calibrated to order.
- All solid state with precision components for long term stability.
- Isolated input output power supply.
- Moulded, flame retardant housing - DIN rail or panel mount.
Information required for Transducer Manufacture
For a Power transducer we need for example:
- Power Supply. 240V,50Hz.
- System configuration. 3 phase 3 wire balanced load.
- Frequency. 50Hz.
- Input current and external CT (if used). 0-5A from 100/5 CT.
- Input voltage and external PT (if used). 0-110V from 11kV/110V PT.
- Output 4-20mA.
- Calibration information:nominate if calibration is for rated current or a nominated watts.
For a 3 phase 100/5A CT and a 11kV/110V PT
W = √3 × 11kV × I × 100A = 1.905MW
if the transducer is calibrated at 5A input.Alternatively we can calibrate at 2MW. In this case the current calibration is
I = ( 2M ÷ ( √3 × 11kV ) ) × ( 5 ÷ 100) = 1.905MW