Alarm Function
Select products that include an Alarm function.
Find Alarm select ⇒ Input ⇒ Output
- 4-20mA
- 4-20mA, Select Output
- 4-20mA 4-Wire
- 4-20mA 4-20mA 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- dc mA/V 4-Wire
- 4-20mA dc mA/V 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- Relay
- 4-20mA Relay, Select Product
- DTA137 Dual Trip Alarm
- STA138 Single Trip Alarm
- TRA173 Triple Trip Alarm
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator


- ac A
- ac A, Select Output
- 4-20mA 4-Wire
- ac A 4-20mA 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- dc mA/V 4-Wire
- ac A dc mA/V 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- Relay

- ac V
- ac V, Select Output
- 4-20mA 4-Wire
- ac V 4-20mA 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- dc mA/V 4-Wire
- ac V dc mA/V 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- Relay

- Conductivity
- Conductivity, Select Output
- Relay
- Conductivity Relay, Select Product
- DTA137 Dual Trip Alarm
- STA138 Single Trip Alarm
- LLD207 Liquid Level Detector


- dc A
- dc A, Select Output
- Relay
- dc A Relay, Select Product
- DCA218 dc Current Alarm


- dc mA/V
- dc mA/V, Select Output
- 4-20mA 4-Wire
- dc mA/V 4-20mA 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- dc mA/V 4-Wire
- dc mA/V dc mA/V 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- Relay
- dc mA/V Relay, Select Product
- DTA137 Dual Trip Alarm
- STA138 Single Trip Alarm
- TRA173 Triple Trip Alarm
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator


- mV
- mV, Select Output
- 4-20mA 4-Wire
- mV 4-20mA 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- dc mA/V 4-Wire
- mV dc mA/V 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- Relay
- mV Relay, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator


- pH/REDOX
- pH/REDOX, Select Output
- Relay
- pH/REDOX Relay, Select Product
- DTA137 Dual Trip Alarm
- STA138 Single Trip Alarm


- Potentiometer
- Potentiometer, Select Output
- 4-20mA 4-Wire
- Potentiometer 4-20mA 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- dc mA/V 4-Wire
- Potentiometer dc mA/V 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- Relay
- Potentiometer Relay, Select Product
- DTA137 Dual Trip Alarm
- STA138 Single Trip Alarm
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator


- Pressure
- Pressure, Select Output
- Relay
- Pressure Relay, Select Product
- PM276 Pressure Monitor
- PM277 Differential Pressure Monitor


- Resistance
- Resistance, Select Output
- 4-20mA 4-Wire
- Resistance 4-20mA 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- dc mA/V 4-Wire
- Resistance dc mA/V 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- Relay
- Resistance Relay, Select Product
- DTA137 Dual Trip Alarm
- STA138 Single Trip Alarm
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator


- RTD
- RTD, Select Output
- 4-20mA 4-Wire
- RTD 4-20mA 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- dc mA/V 4-Wire
- RTD dc mA/V 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- Relay
- RTD Relay, Select Product
- DTA137 Dual Trip Alarm
- STA138 Single Trip Alarm
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator


- Signal Powered
- Signal Powered, Select Output
- 4-20mA 4-Wire
- Signal Powered 4-20mA 4-Wire, Select Product
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- dc mA/V 4-Wire
- Signal Powered dc mA/V 4-Wire, Select Product
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- Relay
- Signal Powered Relay, Select Product
- VPR271 Voltage Presence Relay
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator
- HVR272 High Voltage Relay


- Speed/ Frequency/ Pulse
- Speed/ Frequency/ Pulse, Select Output
- 4-20mA 4-Wire
- Speed/ Frequency/ Pulse 4-20mA 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- dc mA/V 4-Wire
- Speed/ Frequency/ Pulse dc mA/V 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- Relay
- Speed/ Frequency/ Pulse Relay, Select Product
- DTA137 Dual Trip Alarm
- STA138 Single Trip Alarm
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator
- FRA251 Frequency Alarm


- Strain Gauge
- Strain Gauge, Select Output
- Relay
- Strain Gauge Relay, Select Product
- DTA137 Dual Trip Alarm
- STA138 Single Trip Alarm


- Thermocouple
- Thermocouple, Select Output
- 4-20mA 4-Wire
- Thermocouple 4-20mA 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- dc mA/V 4-Wire
- Thermocouple dc mA/V 4-Wire, Select Product
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator

- Relay
- Thermocouple Relay, Select Product
- DTA137 Dual Trip Alarm
- STA138 Single Trip Alarm
- DTI135 Dual Trippoint Isolator
- STI136 Single Trippoint Isolator


- Select an Input (above)

Select products that include an Alarm function.

Alarm Function
The alarm module measures the process variable using the appropriate input circuit for the probe or signal type and compares it with a trip point value to determine when to switch.
Main factors to consider when choosing a alarm module are;
- Power supply used to power the module.
- Input measurement from probe, sensor, voltage, current or process signal.
- Trip action. A direct trip action (DIR) will cause the output relay to energised above the trip-point and a reverse (REV) trip action will cause the relay to be energised below the trip-point.
- Reverse action is usually used in fail safe situations to ensure the correct state of the relay contacts when power fails on the alarm module. Trip-point (TRIP) is usually adjusted by the 15-turn trim potentiometer from the front of the module or set using software.
- Contact rating and type, normally open (NO), normally closed (NC) and change over(CO). Change over contacts give the option of connecting the relays as normally open or normally closed as required. These relay states are when the relay is de-energised or when no power is applied to the module.
- Trip status is indicated by LED to give you a visual indication of the relay status.
- Dead band is used to set a window around the set-point to prevent the relay from continuously switching when close to the set-point. This setting could be factory configured, set with a trim potentiometer(dB) or set using software.
- Switching delay. This could be accomplished by filtering the input signal to give a slower response. In more advanced systems the on delay (continuous trip time before the alarm energises) and off delay (continuous below trip time before the alarm de-energises) can be set independently. This setting could be factory configured, set with a trim potentiometers or set using software.
Alarm Dead Band
Many trip alarms have a dead band adjustment. Dead band (DB) is a common term for relay hysteresis and is usually expressed as percentage of span (%DB).
Dead band does not interfere with the ON switching of the relay. Looking at the direct action example below, we see that dead band is the change of input required to turn the relay OFF.
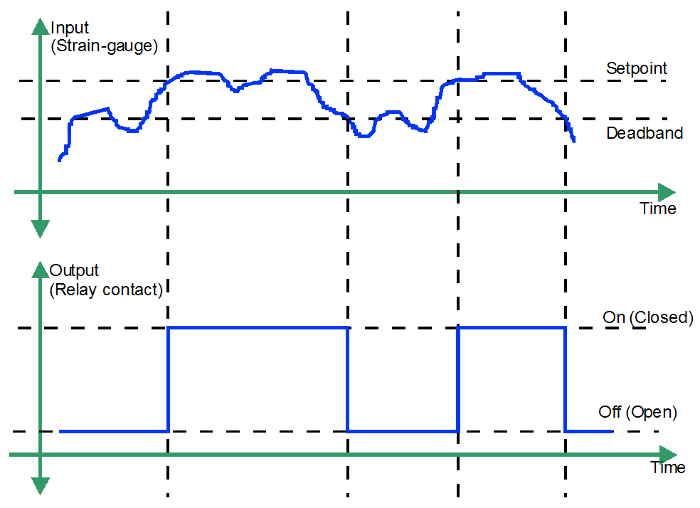
Alarm Dead Band
Lets follow the input path on the diagram. The input begins below the set-point adjustment. The output (relay) only switches ON after the input goes above the set-point.
The input continues to vary above and below the set-point however the output (relay) remains ON until the input falls below the dead band adjustment.
The input now varies above and below the dead band adjustment, however, as we can see, the relay can only be switched ON if the input returns above the set-point.
Dead band may be easier to understand if units are introduced. Lets use an example process where the level of a water tank is monitored.
The set-point is set to comfortable operating water level of 10m. The dead band is set to a minimum water level of 8m. With these settings the outlet valve controlled by the alarm allows water to exist the tank only open if the water level rises above 10m, and will close if the water level falls below 8m. If we wanted to reduce the minimum water level to 6m then we would need to increase the dead band.